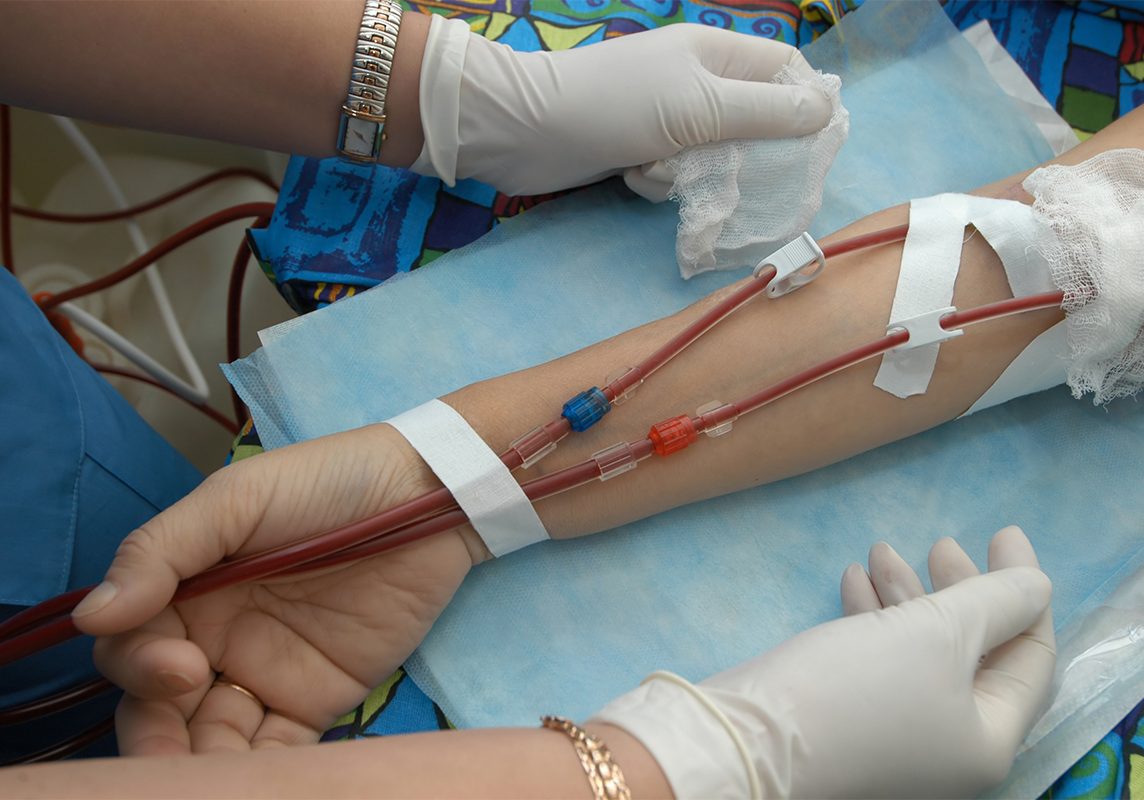
Dialysis has been used to treat patients with kidney problems since the 1940s. Quite simply, dialysis is a procedure where the blood is filtered and purified with the use of a machine. This treatment is used when the kidneys are unable to do their job and it helps to keep the body in balance.
Healthy kidneys would normally prevent extra water, waste and other impurities from accumulating in your body. They also help to regulate blood pressure as well as the levels of sodium, and potassium in the blood.
When a patient's kidneys are unable to function correctly due to disease or injury then the use of dialysis can keep the body functioning correctly.

In Center Hemodialysis
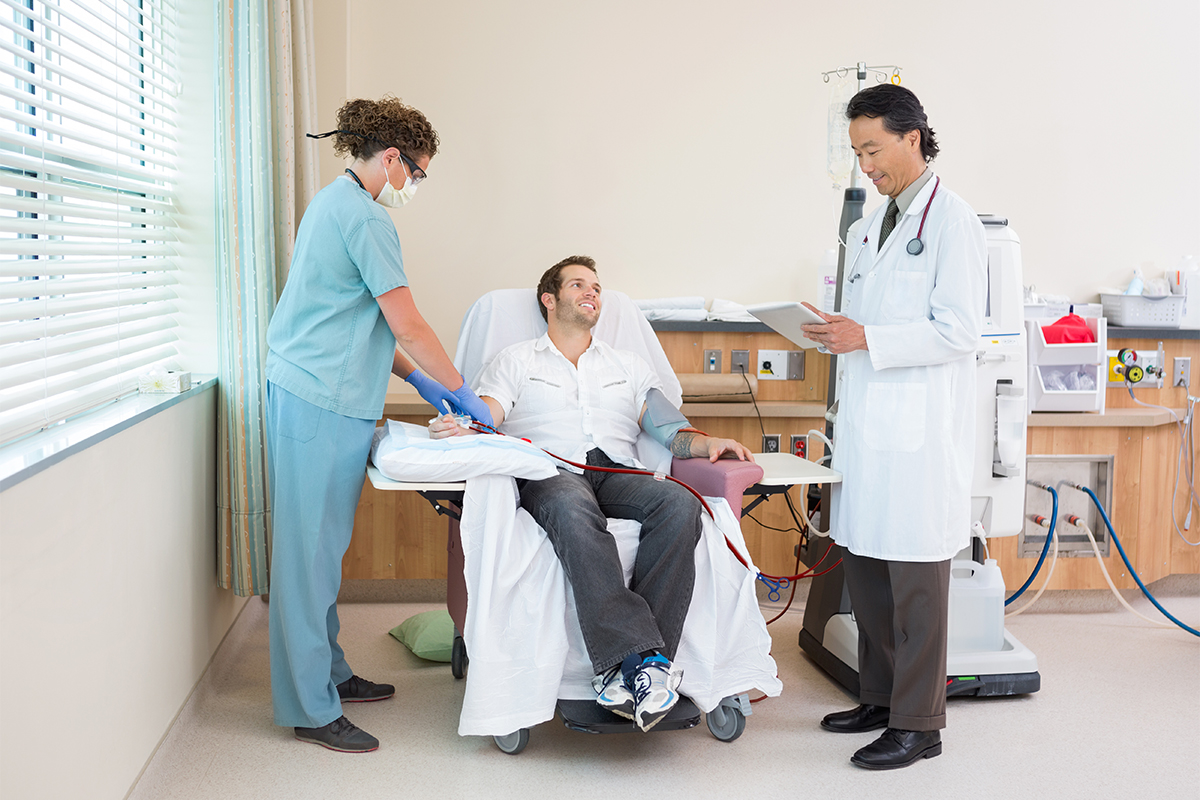
The most common way to treat advanced kidney failure, hemodialysis is the system of removing waste products, chemical substances, and extra fluid from a patient's body through the use of a dialyzer, an artificial kidney.
This process of dialysis is usually done at least three times per week and at a specialized dialysis center. Each session takes an average of four hours to clean a patient's blood.
In order to access your blood there needs to be an "access". This is usually through a fistula, graft, or dialysis catheter.
We see patients for in-center hemodialysis on scheldules of Monday, Wednesday, Friday, or Tuesday, Thursday, Saturday.
We work with the following dialysis centers:
Home Hemodialysis
(HHD) is the option for patients to have hemodialysis at home. This is an option for patients with end-stage renal disease.
This option offers a greater amount of freedom to our patients as well as flexibility and convenience. Dialysis at home will require fewer office visits.

Peritoneal Dialysis
This treatment is for patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). It uses the peritoneum in the abdomen as a membrane to make fluids and other dissolved substances, such as electrolytes, urea, glucose, albumin, etc., are exchanged from the blood.
This fluid is injected through a permanent tube in the abdomen and flushed out either every night while the patient is asleep or at regular exchanges throughout the day.
This option offers patients both flexibility and patient autonomy by giving them the ability to perform dialysis at home.
